Which Best Explains How Earth's Climate Is Impacted by Convection
It also influences Earths climate. EEn112 Explain how the Earths rotation and revolution about the Sun affect its shape and is related to seasons and tides.
Nws Jetstream The Transfer Of Heat Energy
Each individual column in this Hovmoller Diagram is one day of rainfall across Africa 20W-55E averaged by latitude.
. The result of Earths rotation on weather patterns and ocean currents. Which best explains how Earths climate is impacted by convection. Severe thunderstorms are defined as having sustained winds above 93 kilometers 58 miles per hour or unusually large hail and there are two key factors that fuel their formation.
Part of what makes Earth so amenable is its natural greenhouse effect which keeps the planet at a friendly 15 C 59 F on average. Warmed air expands and becomes less dense than cool air so warmed air near the surface of the Earth rises up. It helps keep the planet warm enough for us to survive.
Maps of sea surface temperature anomaly in the Pacific Ocean during a strong. And now scientists have detailed how that process might work according to a new study published. Small changes in the suns brightness can have big impacts on our planets weather and climate.
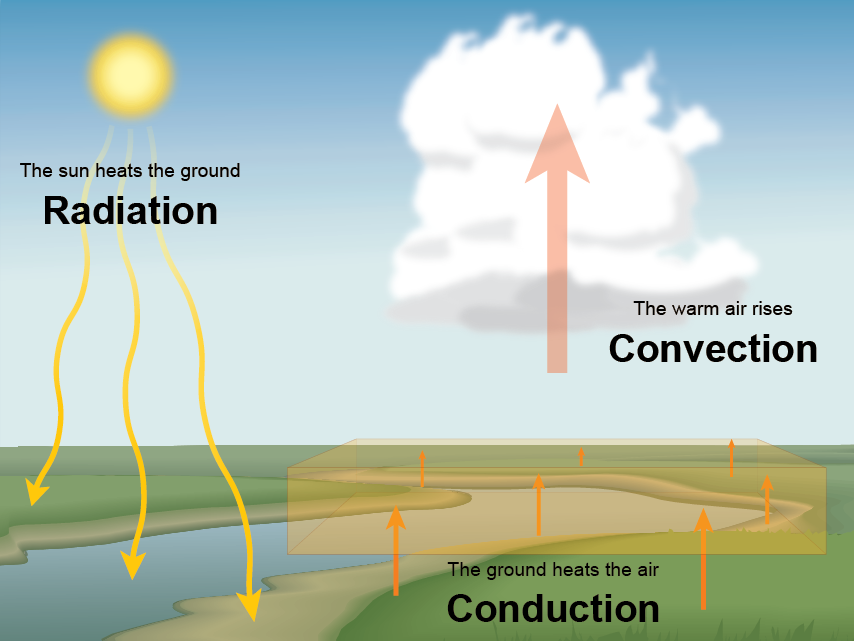
The Sun powers life on Earth. EEn111 Explain the Earths motion through space including precession nutation the barycenter and its path about the galaxy. Convection works by areas of a liquid or gas heating or cooling greater than their surroundings causing differences in temperature.
EEn11 Explain the Earths role as a body in space. Weather and climate are the result of a complex series of interactions between all elements of the Earth system hydrosphere atmosphere biosphere solid Earth but are largely controlled by the interaction between the Earth and Sun. But the warming weve seen over the last few decades is too rapid to be linked to changes in Earth.
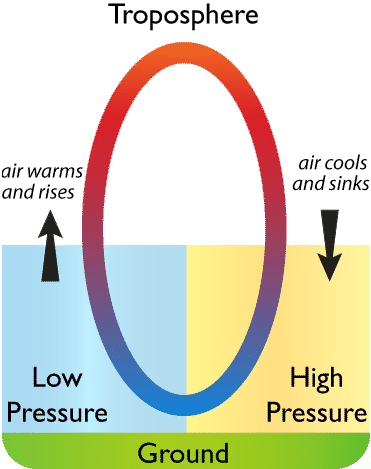
The circulation of air in the earths atmosphere is driven by convection. The study conducted by climate change research scientist Aixue Hu of the National Center for Atmospheric Research and published Monday in the journal Nature Climate Change found that solar. Conduction radiation and convection all play a role in moving heat between Earths surface and the atmosphere.
Cooler air from above sinks and air moves horizontally to replace the rising warm air which we experience as wind over the surface of the Earth. These temperature differences then cause the. March Daffodils in Raleighs Dorothea Dix Park 2021 From The Mountains To The Outer Banks The North Carolina State Climate Office serves as the primary scientific extension resource for weather and climate science for the state of North Carolina.
It cools down as it rises and becomes less dense than the air that is around spreading out and descending again towards the equator. But in the last century or so humans have been interfering with the. For that reason Earth is sometimes called the Goldilocks planet its conditions are not too hot and not too cold but just right to allow life including us to flourish.
9A evaluate heat transfer through Earths subsystems by radiation convection and conduction and include its role in plate tectonics volcanism ocean circulation weather and climate 11A compare the roles of erosion and deposition through the actions of water wind ice gravity and igneous activity by lava in constantly reshaping Earths. A cross between a map and a graph the figure is known today as a Hovmöller Diagram. The heat source for our planet is the sun.
Convection helps cool the Earth and the atmosphere around it. There are three ways heat is transferred into and through the atmosphere. Neutral indicates that conditions are near their long-term average.
Convective available potential energy CAPE and strong wind shear. Convection helps move thermal energy around the Earth. The Coriolis effect makes storms swirl clockwise in the Southern hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere.
Near the equator of the earth the sun heats the air which becomes less dense and rises upwards. Encyclopedia of Solid Earth Geophysics Mantle Convection David Bercovici Figure 1. Climate change will continue to have a significant impact on ecosystems and organisms though they are not impacted equally.
The distribution of solar radiation on the Earths surface regulates the length and order of the seasons. El Niño the warm phase and La Niña the cool phase lead to significant differences from the average ocean temperatures winds surface pressure and rainfall across parts of the tropical Pacific. Changes in the weather-The cool air and breeze occurring near to a beach are all the effects of convection currents.
Graphic renditions of cut aways of Earths structure showing crust mantle and core left and of the convecting mantle right. Thus ocean currents regulate global climate helping to counteract the uneven distribution of solar radiation reaching Earths surface. Conduction directly affects air.
These three processes transfer the equivalent of 53 percent of the incoming solar energy to the atmosphere. This transfer of heat because of density differences in air is called convection. Evaporation and convection transfer 25 and 5 percent of incoming solar energy from the surface to the atmosphere.
Convection continuously pumps cool energy through the oceans. In 1949 a scientist by the name of Ernest Hovmöller created a diagram that excels at showing movement in static pictures Hovmöller 1949. Without currents in the ocean regional temperatures would be more extremesuper hot at the equator and frigid toward the polesand much less of Earths land would be habitable.
The relevant dimensions are that the Earths average radius is 6371km. Convection stops the flow of cool air and maintains warm weather. These are caused due to the difference in the water density and the temperature.
Energy from the sun is transferred through space and through the earths atmosphere to the earths surface. Convection currents occurring in the ocean The Oceanic currents are also the convection currents. The office achieves its mission through climate science monitoring education extension and research.
Earths interior is cooling faster than expected. The Arctic is one of the ecosystems most vulnerable to the effects of climate change as it is warming at least twice the rate of the global average and melting land ice sheets and glaciers contribute dramatically offsite. Since air is a poor conductor most energy transfer by conduction occurs right near Earths surface.
Clouds aerosols water vapor and ozone directly absorb 23 percent of incoming solar energy. Researchers have demonstrated in the lab how well a mineral common at the boundary between the Earths core and mantle conducts heat. It relates to how warm moist.
CAPE is a measure of how much raw energy is available for storms. We know subtle changes in Earths orbit around the Sun are responsible for the comings and goings of the past ice ages. Since this energy warms the earths surface and atmosphere some of it is or becomes heat energy.
The weather changes on a daily basis are also affected by these currents.

Circulation In The Atmosphere Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation
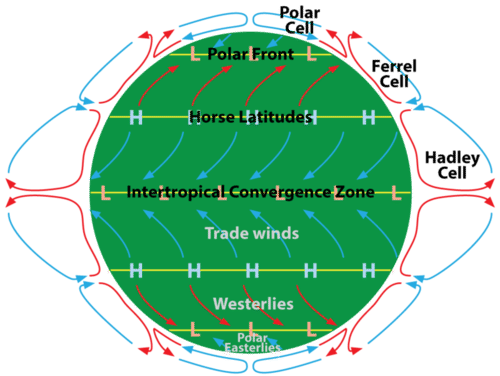
Circulation In The Atmosphere Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation

No comments for "Which Best Explains How Earth's Climate Is Impacted by Convection"
Post a Comment