Describe the Alternation of Generations in Plants
Briefly describe alternation of generations in plants. Alternation of generations is sexual reproduction in plants as it involves the creation and combining of sex cells.

Alternation Of Generations Plant Definition Life Cycle Biology Dictionary
It is not always easy to observe however.

. As plant groups have evolved complexity from bryophytes moss to angiosperms. Take care not to confuse the sporophytes produces haploid spores alternation of generations in plants with the The gametophyte produces reproductive cells that can develop into haploid and diploid stages in the life cycles haploid gametes by mitosis. View the full answer.
Hence the whole mechanism is called alternation of generations. Plants and some animals are capable of reproducing both asexually and sexually. The gametes fuse to form a zygote that develops into a sporophyte.
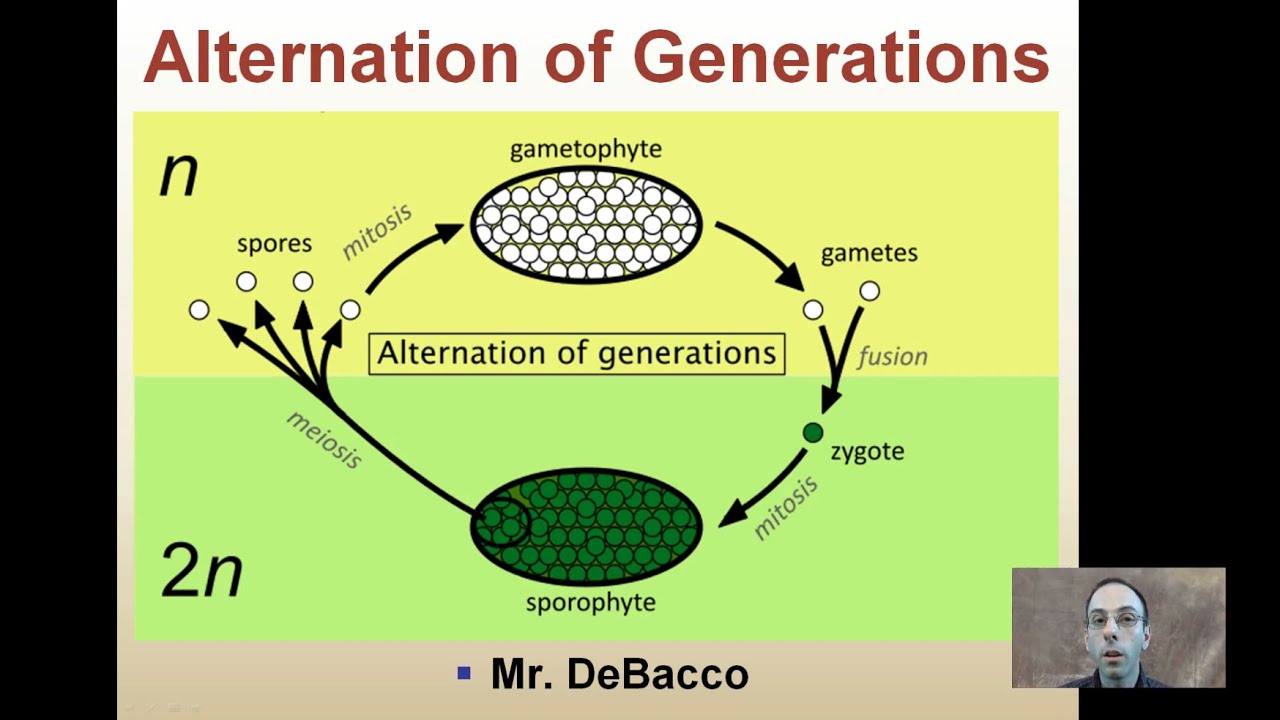
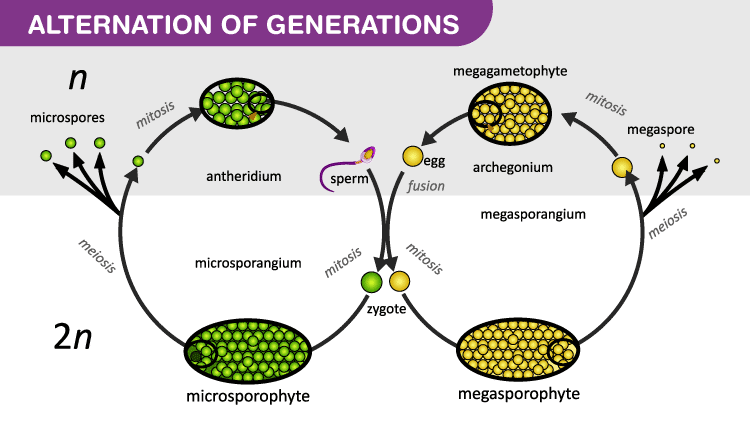
The sporangium undergoes meiosis and forms haploid spores. A multicellular gametophyte which is haploid with n chromosomes alternates with a multicellular sporophyte which is diploid with 2n chromosomes made up of n pairs. The dominant plant is a diploid sporophyte which forms haploid spores.
All embryophytes and some algae undergo this process. They germinate on the ground into a gametophyte which produces haploid male and female gametes. The diploid sporophyte has a structure called sporangium.
Meiosis and fertilization help its maintainance. Both forms are multicellular. The asexual phase produces spores and is called the sporophyte generation.
Answer and Explanation. The life cycle of a plant is called the alternation of generations. The term alternation of generations is used to describe an alternation of forms in the life cycle of plants and some protists.
There is a rotation between these generations. All land plants undergo an alternation of generations between multicellular haploid gametophyte and diploid sporophyte life stages. Be sure to include a description of what alternation of generations is the names of the generations and their chromosome number.
In a paragraph describe alternation of generations in ferns. In algae fungi and plants alternation of generations is common. Describe alternation of generations in plants using the words.
In mosses and their household bryophytes the haploid gametophyte is the dominant technology and the diploid sporophytes are sporangium bearing stalks growing from the gametophytes. Biology questions and answers. Alternation of generations describes a plants life cycle as it alternates between a sexual phase or generation and an asexual phase.
The sexual generation in plants produces gametes or sex cells and is called the gametophyte generation. A new friends life cycle begins with a mature Fern which produces spores. So one complete life cycle of a plant includes two generations that alternate with each other.
If there is no alternation of generation maintainace of constancy of chromosomes is not possible and specificity of chracters of species will be lost. Plant Life Cycle. The other form is haploid with only one set of chromosomes.
However increasing recognition of the potential for selection. The alternation of generations is an important concept in the evolution of flowersAll land plant life have alternation of generations. Haploid - Diploid - Gametophyte - Sporophyte - Gametes - Zygote -.
It is a complex cycle with many different life stages that can be be both diploid and haploid. A new haploid organism. Meiosis in a mature related to plants.
Alternation of generations is a term primarily used to describe the life cycle of plants. The gametophyte has the reproductive organs which. Alternation of generations describes a plants life cycle as it alternates between a sexual phase or generation and an asexual phase.
Haploid and diploid generations alternately formed in the life cycle of plants and animals are called alternation of generation. Alternation of generations also called metagenesis or heterogenesis in biology the alternation of a sexual phase and an asexual phase in the life cycle of an organism. It consists of a multicellular haploid sexual phase the gametophyte which has a single set of chromosomes alternating with a multicellular diploid asexual phase the sporophyte which has two sets of chromosomes.
The life cycle of a fern involved both asexual and sexual reproduction reproduction. Plants has a peculiar lifecycle wherein they have two generations where one is haploid and the other is diploid. The diploid stage is called Sporophyte and the haploid stage is called the Ga.
The two phases or generations are often morphologically and sometimes chromosomally distinct. Plant life cycle and alternation of generation. Alternation of Generations This term refers to the life cycle of most plants in which the generations alternate between haploid gametophytes and diploid sporophytes.
Alternation of generations is seen in both vascular and non-vascular plants. The spore develops into a gametophyte which is haploid in nature. Each is called one generation.
One form is diploid with 2 n chromosomes. The alternation of generations include the following stages. This is called alternation of generations.
The diploid sporophyte phase is the dominant life stage for the majority of land plants and has historically received the lions share of attention from the scientific community. Describe the Alternation of Generations Life Cycle found in flowering plants. The two generations or life cycles that occur are called the sporophyte generation and the gametophyte generation.
A mature sporophyte produces haploid spores by meiosis a process which. Alternation of generations is the predominant type of life cycle in plants and algae. Label the image below to describe the alternation of generations exhibited by plants gamelophyte m Zygolo 2n Meiosis Mitosis gametis n sporoployle 2n spore n diploid 2n Fertilization haploid n sporangium 2 Mitosis Mitosis.
Alternation of Generations Plant vs Animal Life Cycles.

Alternation Of Generations Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
No comments for "Describe the Alternation of Generations in Plants"
Post a Comment